Getting Started on Okteto Cloud with Java
Okteto Cloud gives instant access to secure Kubernetes namespaces to enable developers to code, build, and run Kubernetes applications entirely in the cloud.
This tutorial will show you how to develop and debug a Java sample application running in Okteto Cloud.
Prerequisites
- Install the latest version of the Okteto CLI. . Follow this guide if you haven't done it yet.
- Configure access to your Okteto Cloud Namespace using the Okteto CLI or using the Okteto Cloud UI.
Step 1: Deploy the Java Sample App
Get a local version of the Java Sample App by executing the following commands:
Maven
$ git clone https://github.com/okteto/java-maven-getting-started
$ cd java-maven-getting-started
Gradle
$ git clone https://github.com/okteto/java-gradle-getting-started
$ cd java-gradle-getting-started
At the root of the directory, you'll find the okteto.yaml file. This describes how to build and deploy the Node Sample App.
Maven
build:
hello-world:
image: okteto.dev/java-maven-hello-world:1.0.0
context: .
deploy:
- kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
Gradle
build:
hello-world:
image: okteto.dev/java-gradle-hello-world:1.0.0
context: .
deploy:
- kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
Deploy your development environment by executing:
$ okteto deploy --build
Maven
i Using cindy @ cloud.okteto.com as context
i Building image for service 'hello-world'
i Building the image 'okteto.dev/java-maven-hello-world:1.0.0' in tcp://buildkit.cloud.okteto.net:1234...
[+] Building 5.9s (11/11) FINISHED
...
✓ Image 'registry.cloud.okteto.net/cindy/java-maven-hello-world:1.0.0' successfully pushed
i Running kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
deployment.apps/hello-world created
service/hello-world created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/hello-world created
✓ Development environment 'java-maven-getting-started' successfully deployed
i Run 'okteto up' to activate your development container
Gradle
i Using cindy @ cloud.okteto.com as context
i Building image for service 'hello-world'
i Building the image 'okteto.dev/java-gradle-hello-world:1.0.0' in tcp://buildkit.cloud.okteto.net:1234...
[+] Building 5.9s (11/11) FINISHED
...
✓ Image 'registry.cloud.okteto.net/cindy/java-gradle-hello-world:1.0.0' successfully pushed
i Running kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
deployment.apps/hello-world created
service/hello-world created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/hello-world created
✓ Development environment 'java-gradle-getting-started' successfully deployed
i Run 'okteto up' to activate your development container
Log into Okteto Cloud and click on the URL of the application:
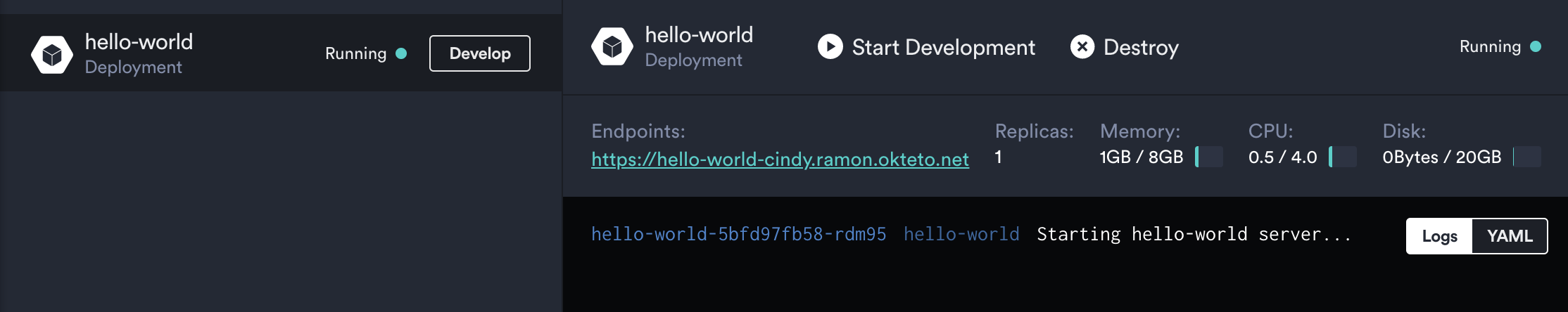
Did you notice that you're accessing your application through an HTTPs endpoint? This is because Okteto Cloud will automatically create them for you when you deploy your application. Cool no 😎?
Step 2: Activate your development container
The dev section defines how to activate a development container for the Java
Maven
dev:
hello-world:
image: okteto/maven:3
command: bash
sync:
- .:/usr/src/app
forward:
- 5005:5005
volumes:
- /root/.m2
Gradle
dev:
hello-world:
image: okteto/gradle:6.5
command: bash
sync:
- .:/usr/src/app
forward:
- 5005:5005
volumes:
- /home/gradle/.gradle
The hello-world key matches the name of the hello world Deployment. The meaning of the rest of fields is:
image: the image used by the development container. More information on development images herecommand: the start command of the development containersync: the folders that will be synchronized between your local machine and the development containerforward: a list of ports to forward from your development containervolumes: a list of paths in your development container to be mounted as persistent volumes. This is useful to persist the maven/gradle caches.
Also, note that there is a .stignore file to indicate which files shouldn't be synchronized to your development container.
This is useful to avoid synchronizing binaries, build artifacts, or git metadata.
Step 3: Activate your development container
Next, execute the following command to activate your development container:
$ okteto up
✓ Persistent volume successfully attached
✓ Images successfully pulled
✓ Files synchronized
Namespace: cindy
Name: hello-world
Forward: 5005 -> 5005
Welcome to your development container. Happy coding!
cindy:hello-world app>
Working in your development container is the same as working on your local machine. Start the application by running the following command:
Maven
default:hello-world app> mvn spring-boot:run
Gradle
default:hello-world app> gradle bootRun
The first time you run the application, Maven/Gradle will compile your application. Wait for this process to finish.
Go back to the browser and reload the page to test that your application is running.
Step 4: Develop directly on Okteto Cloud
Open src/main/java/com/okteto/helloworld/RestHelloWorld.java in your favorite local IDE and modify the response message on line 11 to be Hello world from Okteto!. Save your changes.
package com.okteto.helloworld;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class RestHelloWorld {
@GetMapping("/")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello world from Okteto!";
}
}
Your IDE will auto compile only the necessary *.class files which will be synchronized by Okteto to your application in Okteto Cloud. Take a look at the development container shell and notice how the changes are detected by Spring Boot and automatically hot reloaded.
Import the
spring-boot-devtoolsdependency to automatically restart your Java application whenever a file is changed.
Go back to the browser and reload the page. Your code changes were instantly applied. No commit, build, or push required 😎!
Step 5: Debug directly on Okteto Cloud
Okteto enables you to debug your applications directly from your favorite IDE. Let's take a look at how that works in Eclipse, one of the most popular IDEs for Java development.
Add the following JVM arguments in the Gradle/Maven configuration files to enable remote debugging in your Java application:
-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
Open the Debug configuration dialog, add a new Remote Java Application debug configuration, and point it to localhost:5005:
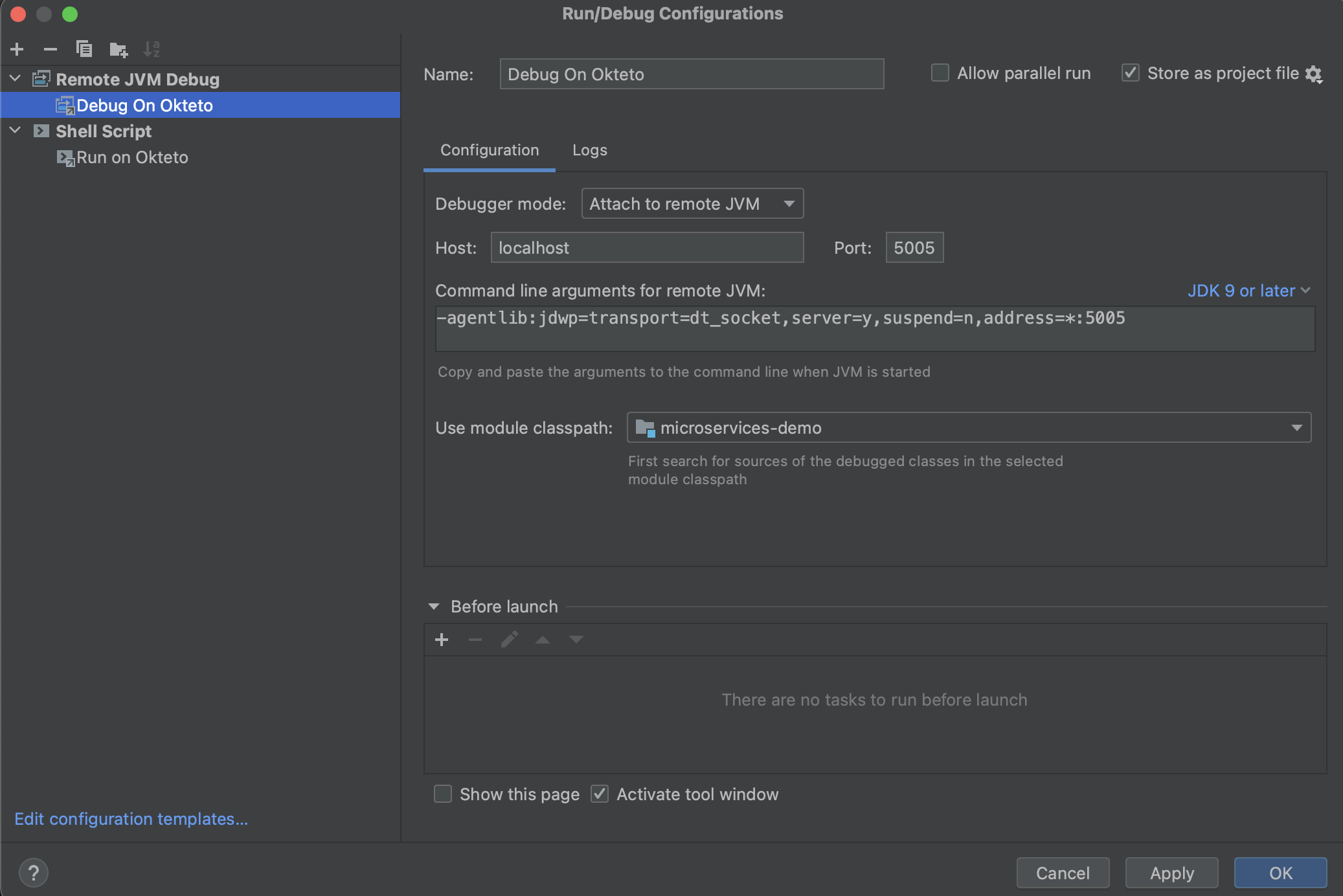
Click the Debug button to start a debugging session. Add a breakpoint on src/main/java/es/okteto/helloworld/RestHelloWorld.java, line 11. Go back to the browser and reload the page. The execution will halt at your breakpoint. You can then inspect the request, the available variables, etc...
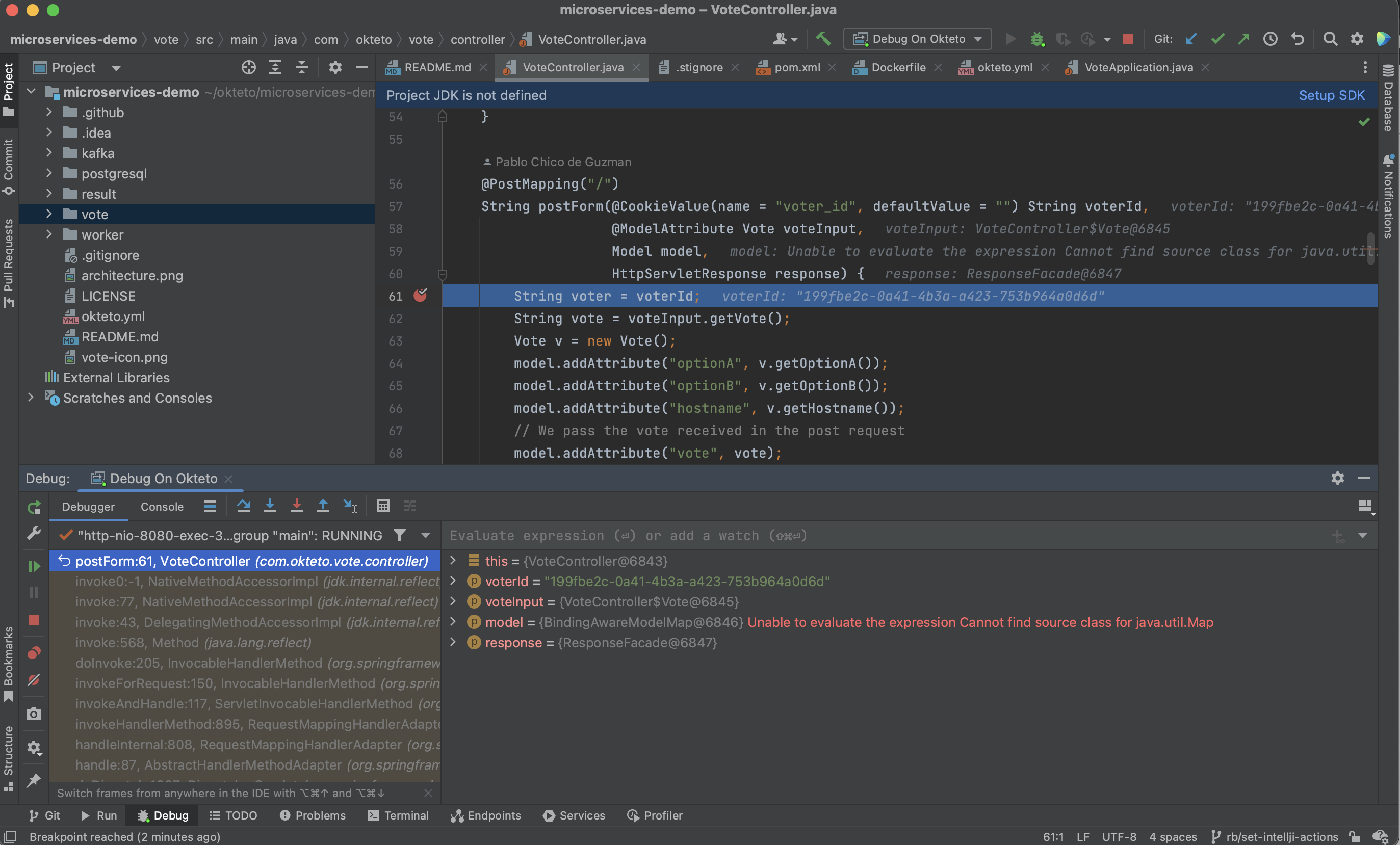
Your code is executing in Okteto Cloud, but you can debug it from your local machine without any extra services or tools. Pretty cool no? 😉
Next steps
Congratulations, you just developed your first application in Okteto Cloud 🚀.
Okteto lets you develop your applications directly on Kubernetes. This way you can:
- Eliminate integration issues by developing in a realistic environment
- Test your application end to end as fast as you type code
- No more CPU cycles wasted in your machine. Develop at the speed of the cloud!
Find more advanced samples with Okteto in this repository or join our community to ask questions and share your feedback.